What is Swing?
Java Swing is a lightweight Graphical User Interface (GUI) toolkit that includes a rich set of widgets. It includes package lets you make GUI components for your Java applications, and It is platform independent.
The Swing library is built on top of the Java Abstract Widget Toolkit (AWT), an older, platform dependent GUI toolkit. You can use the Java GUI components like button, textbox, etc. from the library and do not have to create the components from scratch.
In this tutorial, you will learn-
- What is Swing?
- What is a container class?
- GUI Example
- Layout Manager
- BorderLayout
- FlowLayout
- GridBagLayout
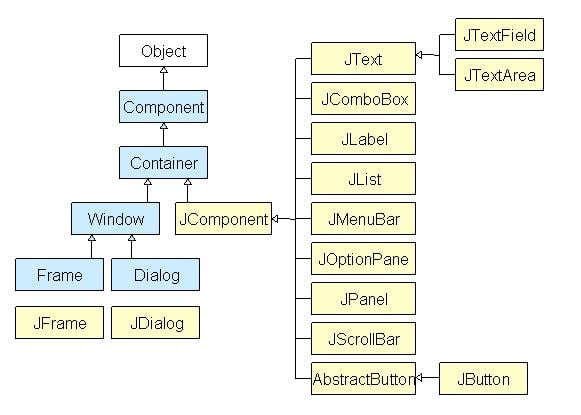
All components in swing are JComponent which can be added to container classes.
What is a container class?
Container classes are classes that can have other components on it. So for creating a GUI, we need at least one container object. There are 3 types of containers.
- Panel: It is a pure container and is not a window in itself. The sole purpose of a Panel is to organize the components on to a window.
- Frame: It is a fully functioning window with its title and icons.
- Dialog: It can be thought of like a pop-up window that pops out when a message has to be displayed. It is not a fully functioning window like the Frame.
Java GUI Example
Example: To learn to design GUI in Java
Step 1) Copy the following code into an editor
Step 1) Copy the following code into an editor
import javax.swing.*;
class gui{
public static void main(String args[]){
JFrame frame = new JFrame("My First GUI");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(300,300);
JButton button = new JButton("Press");
frame.getContentPane().add(button); // Adds Button to content pane of frame
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Step 2) Save, Compile, and Run the code.
Step 3) Now let's Add a Button to our frame. Copy following code into an editor
Step 3) Now let's Add a Button to our frame. Copy following code into an editor
import javax.swing.*;
class gui{
public static void main(String args[]){
JFrame frame = new JFrame("My First GUI");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(300,300);
JButton button1 = new JButton("Press");
frame.getContentPane().add(button1);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Step 4) Execute the code. You will get a big button

Step 5) How about adding two buttons? Copy the following code into an editor.
import javax.swing.*;
class gui{
public static void main(String args[]){
JFrame frame = new JFrame("My First GUI");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(300,300);
JButton button1 = new JButton("Button 1");
JButton button2 = new JButton("Button 2");
frame.getContentPane().add(button1);
frame.getContentPane().add(button2);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Step 6) Save , Compile , and Run the program.
Step 7) Unexpected output =? Buttons are getting overlapped.
Step 7) Unexpected output =? Buttons are getting overlapped.
Java Layout Manger
The Layout manager is used to layout (or arrange) the GUI java components inside a container.There are many layout managers, but the most frequently used are-
Java BorderLayout
A
BorderLayout places components in up to five areas: top, bottom, left, right, and center. It is the default layout manager for every java JFrame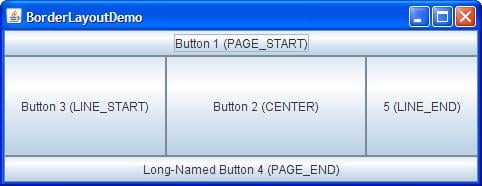
Java FlowLayout
FlowLayout is the default layout manager for every JPanel. It simply lays out components in a single row one after the other.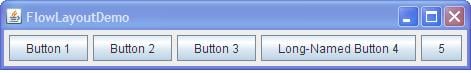
Java GridBagLayout
It is the more sophisticated of all layouts. It aligns components by placing them within a grid of cells, allowing components to span more than one cell.
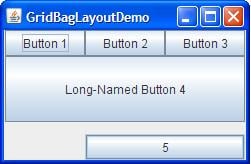
Step 8) How about creating a chat frame like below?

Try to code yourself before looking at the program below.
//Usually you will require both swing and awt packages
// even if you are working with just swings.
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
class gui {
public static void main(String args[]) {
//Creating the Frame
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Chat Frame");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(400, 400);
//Creating the MenuBar and adding components
JMenuBar mb = new JMenuBar();
JMenu m1 = new JMenu("FILE");
JMenu m2 = new JMenu("Help");
mb.add(m1);
mb.add(m2);
JMenuItem m11 = new JMenuItem("Open");
JMenuItem m22 = new JMenuItem("Save as");
m1.add(m11);
m1.add(m22);
//Creating the panel at bottom and adding components
JPanel panel = new JPanel(); // the panel is not visible in output
JLabel label = new JLabel("Enter Text");
JTextField tf = new JTextField(10); // accepts upto 10 characters
JButton send = new JButton("Send");
JButton reset = new JButton("Reset");
panel.add(label); // Components Added using Flow Layout
panel.add(label); // Components Added using Flow Layout
panel.add(tf);
panel.add(send);
panel.add(reset);
// Text Area at the Center
JTextArea ta = new JTextArea();
//Adding Components to the frame.
frame.getContentPane().add(BorderLayout.SOUTH, panel);
frame.getContentPane().add(BorderLayout.NORTH, mb);
frame.getContentPane().add(BorderLayout.CENTER, ta);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}

No comments:
Post a Comment